Diagnosis
| Blood test | Days |
|---|---|
| Antibody test (rapid test, ELISA 3rd gen) | 23–90 |
| Antibody and p24 antigen test (ELISA 4th gen) | 18–45 |
| PCR | 10–33 |
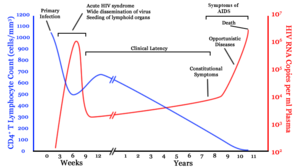
HIV/AIDS is diagnosed via laboratory testing and then staged based on the presence of certain signs or symptoms. HIV screening is recommended by the United States Preventive Services Task Force for all people 15 years to 65 years of age, including all pregnant women. Additionally, testing is recommended for those at high risk, which includes anyone diagnosed with a sexually transmitted illness. In many areas of the world, a third of HIV carriers only discover they are infected at an advanced stage of the disease when AIDS or severe immunodeficiency has become apparent.
HIV testing
Most people infected with HIV develop specific antibodies (i.e. seroconvert) within three to twelve weeks after the initial infection. Diagnosis of primary HIV before seroconversion is done by measuring HIV-RNA or p24 antigen. Positive results obtained by antibody or PCR testing are confirmed either by a different antibody or by PCR.
Antibody tests in children younger than 18 months are typically inaccurate, due to the continued presence of maternal antibodies. Thus HIV infection can only be diagnosed by PCR testing for HIV RNA or DNA, or via testing for the p24 antigen. Much of the world lacks access to reliable PCR testing, and people in many places simply wait until either symptoms develop or the child is old enough for accurate antibody testing. In sub-Saharan Africa between 2007 and 2009, between 30% and 70% of the population were aware of their HIV status. In 2009, between 3.6% and 42% of men and women in sub-Saharan countries were tested; this represented a significant increase compared to previous years.
Classifications
Two main clinical staging systems are used to classify HIV and HIV-related disease for surveillance purposes: the WHO disease staging system for HIV infection and disease, and the CDC classification system for HIV infection. The CDC's classification system is more frequently adopted in developed countries. Since the WHO's staging system does not require laboratory tests, it is suited to the resource-restricted conditions encountered in developing countries, where it can also be used to help guide clinical management. Despite their differences, the two systems allow comparison for statistical purposes.
The World Health Organization first proposed a definition for AIDS in 1986. Since then, the WHO classification has been updated and expanded several times, with the most recent version being published in 2007. The WHO system uses the following categories:
- Primary HIV infection: May be either asymptomatic or associated with acute retroviral syndrome
- Stage I: HIV infection is asymptomatic with a CD4+ T cell count (also known as CD4 count) greater than 500 per microlitre (µl or cubic mm) of blood. May include generalized lymph node enlargement.
- Stage II: Mild symptoms, which may include minor mucocutaneous manifestations and recurrent upper respiratory tract infections. A CD4 count of less than 500/µl
- Stage III: Advanced symptoms, which may include unexplained chronic diarrhea for longer than a month, severe bacterial infections including tuberculosis of the lung, and a CD4 count of less than 350/µl
- Stage IV or AIDS: severe symptoms, which include toxoplasmosis of the brain, candidiasis of the esophagus, trachea, bronchi, or lungs, and Kaposi's sarcoma. A CD4 count of less than 200/µl
The United States Center for Disease Control and Prevention also created a classification system for HIV, and updated it in 2008 and 2014. This system classifies HIV infections based on CD4 count and clinical symptoms, and describes the infection in five groups. In those greater than six years of age it is:
- Stage 0: the time between a negative or indeterminate HIV test followed less than 180 days by a positive test.
- Stage 1: CD4 count ≥ 500 cells/µl and no AIDS-defining conditions.
- Stage 2: CD4 count 200 to 500 cells/µl and no AIDS-defining conditions.
- Stage 3: CD4 count ≤ 200 cells/µl or AIDS-defining conditions.
- Unknown: if insufficient information is available to make any of the above classifications.
For surveillance purposes, the AIDS diagnosis still stands even if, after treatment, the CD4+ T cell count rises to above 200 per µL of blood or other AIDS-defining illnesses are cured.
Comments
Post a Comment